Matplotlib Markers
Markers
You can use the keyword argument marker to
emphasize each point with a specified marker:
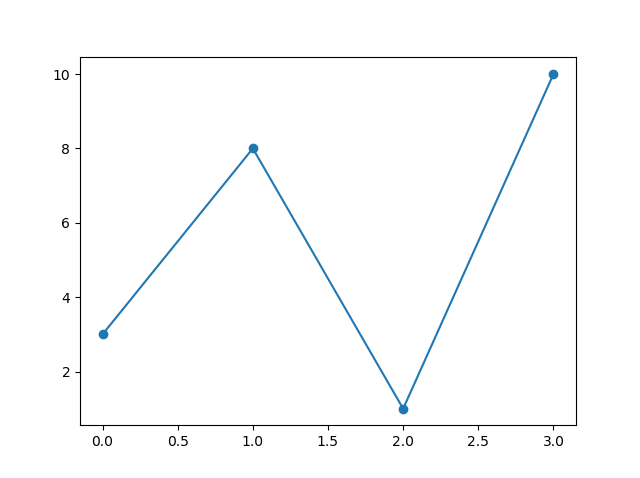
Example
Mark each point with a circle:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
ypoints = np.array([3, 8, 1, 10])
plt.plot(ypoints, marker = 'o')
plt.show()
Result:
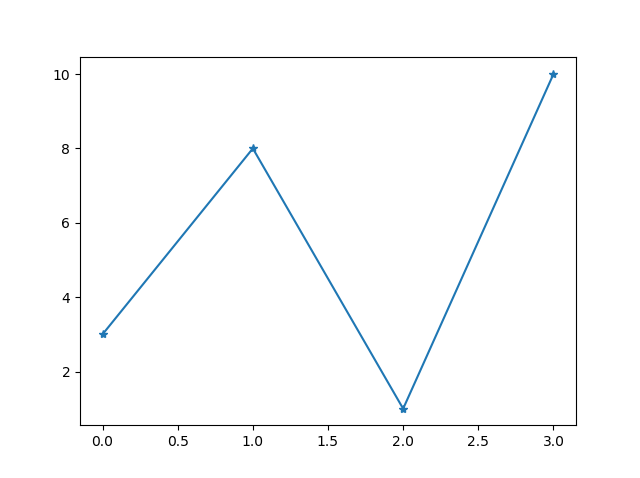
Example
Mark each point with a star:
...
plt.plot(ypoints, marker = '*')
...
Result:
Marker Reference
You can choose any of these markers:
| Marker | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 'o' | Circle | Try it » |
| '*' | Star | Try it » |
| '.' | Point | Try it » |
| ',' | Pixel | Try it » |
| 'x' | X | Try it » |
| 'X' | X (filled) | Try it » |
| '+' | Plus | Try it » |
| 'P' | Plus (filled) | Try it » |
| 's' | Square | Try it » |
| 'D' | Diamond | Try it » |
| 'd' | Diamond (thin) | Try it » |
| 'p' | Pentagon | Try it » |
| 'H' | Hexagon | Try it » |
| 'h' | Hexagon | Try it » |
| 'v' | Triangle Down | Try it » |
| '^' | Triangle Up | Try it » |
| '<' | Triangle Left | Try it » |
| '>' | Triangle Right | Try it » |
| '1' | Tri Down | Try it » |
| '2' | Tri Up | Try it » |
| '3' | Tri Left | Try it » |
| '4' | Tri Right | Try it » |
| '|' | Vline | Try it » |
| '_' | Hline | Try it » |
Format Strings fmt
You can use also use the shortcut string notation parameter to specify the marker.
This parameter is also called fmt, and is written with this syntax:
marker|line|color
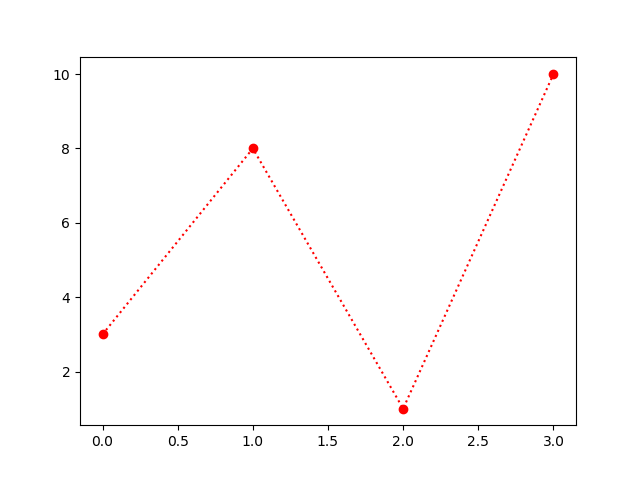
Example
Mark each point with a circle:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
ypoints = np.array([3, 8, 1, 10])
plt.plot(ypoints, 'o:r')
plt.show()
Result:
The marker value can be anything from the Marker Reference above.
The line value can be one of the following:
Line Reference
| Line Syntax | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| '-' | Solid line | Try it » |
| ':' | Dotted line | Try it » |
| '--' | Dashed line | Try it » |
| '-.' | Dashed/dotted line | Try it » |
Note: If you leave out the line value in the fmt parameter, no line will be plottet.
The short color value can be one of the following:
Color Reference
| Color Syntax | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 'r' | Red | Try it » |
| 'g' | Green | Try it » |
| 'b' | Blue | Try it » |
| 'c' | Cyan | Try it » |
| 'm' | Magenta | Try it » |
| 'y' | Yellow | Try it » |
| 'k' | Black | Try it » |
| 'w' | White | Try it » |
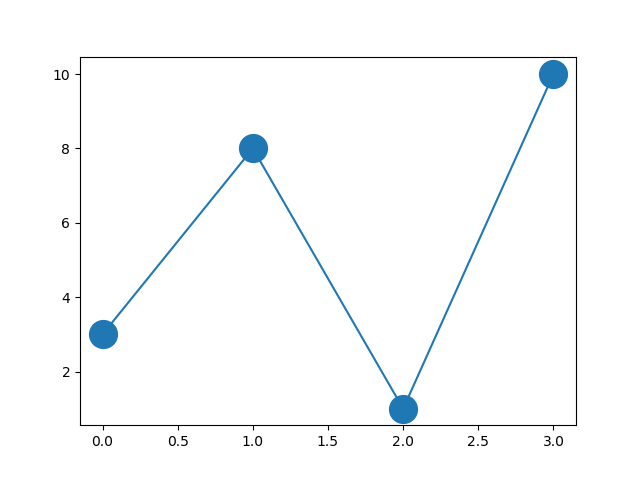
Marker Size
You can use the keyword argument markersize or the
shorter version, ms to set the size of the markers:
Example
Set the size of the markers to 20:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
ypoints = np.array([3, 8, 1, 10])
plt.plot(ypoints, marker = 'o', ms = 20)
plt.show()
Result:
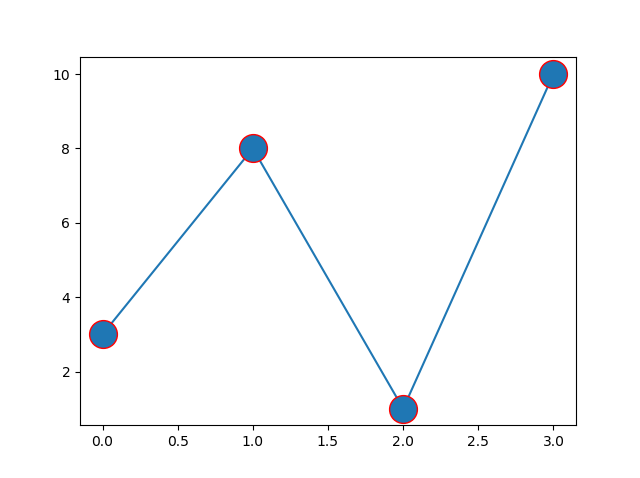
Marker Color
You can use the keyword argument markeredgecolor or
the shorter mec to set the color of the
edge of the markers:
Example
Set the EDGE color to red:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
ypoints = np.array([3, 8, 1, 10])
plt.plot(ypoints, marker = 'o', ms = 20, mec = 'r')
plt.show()
Result:
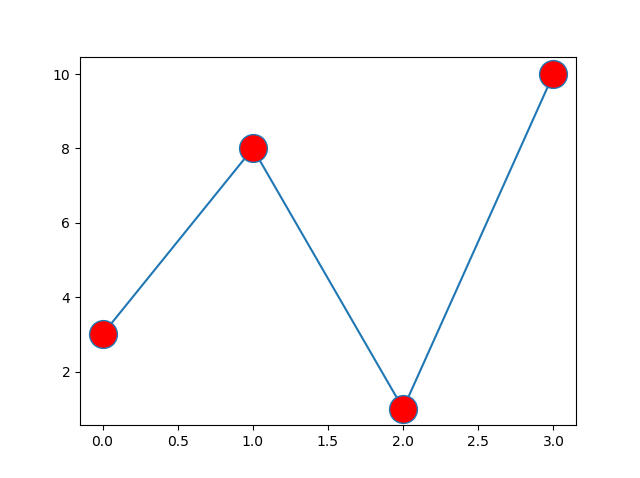
You can use the keyword argument markerfacecolor or
the shorter mfc to set the color inside the edge of the markers:
Example
Set the FACE color to red:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
ypoints = np.array([3, 8, 1, 10])
plt.plot(ypoints, marker = 'o', ms = 20, mfc = 'r')
plt.show()
Result:
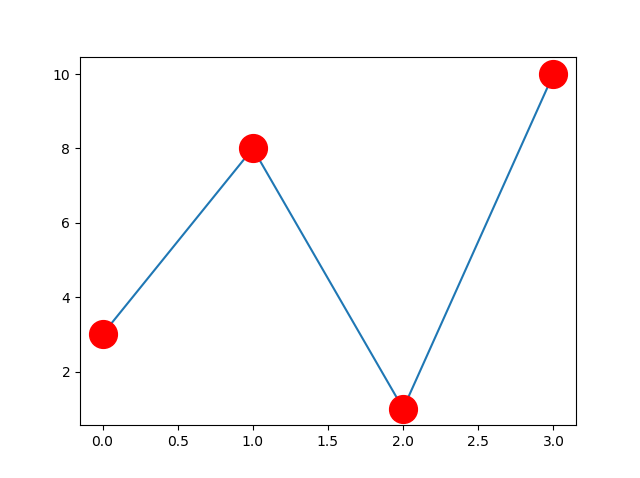
Use both the mec and mfc arguments to color of the entire marker:
Example
Set the color of both the edge and the face to red:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
ypoints = np.array([3, 8, 1, 10])
plt.plot(ypoints, marker = 'o', ms = 20, mec = 'r', mfc = 'r')
plt.show()
Result:
You can also use Hexadecimal color values:
Example
Mark each point with a beautiful green color:
...
plt.plot(ypoints, marker = 'o', ms = 20, mec = '#4CAF50', mfc = '#4CAF50')
...
Result:
Or any of the 140 supported color names.
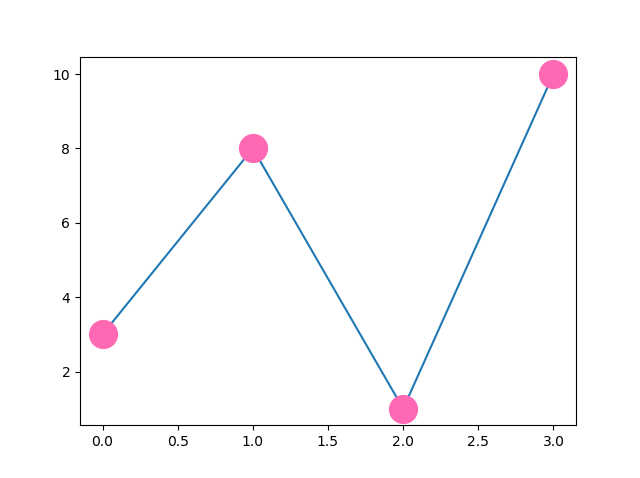
Example
Mark each point with the color named "hotpink":
...
plt.plot(ypoints, marker = 'o', ms = 20, mec = 'hotpink', mfc = 'hotpink')
...
Result: